 Introduction
Introduction
Why yet another framework?
- Use strongest messaging solution to provide realtime features. RabbitMQ instead Socket IO only approach (like Feather.js)
- Production grade built in features like:
- Application stats Notification
- Application logging
- Support for MongoDB
- MS SQl and MySQL databases
- Implement Commom CRUD Service API for Mongo and SQL based servers
- Enforce a well defined message contract to be used as AMQP communication standard
- Ability to restart/stop application easily inside application scope
- easily deploy to production using pm2
- application metrics
- Full ES6 development environment
- Enforces Javascript development standards
- Keep developers focused on business logic instead application stack
Back to Documentation main page
Key Concepts to understand this framework
Component based software engineering
It is a reuse-based approach to defining, implementing and composing loosely coupled independent components into systems.
Software engineering practitioners regard components as part of the starting platform for service-orientation.
All system processes are placed into separate components so that all of the data and functions inside each component are semantically related (just as with the contents of classes). Because of this principle, it is often said that components are modular and cohesive.
With regard to system-wide co-ordination, components communicate with each other via interfaces. When a component offers services to the rest of the system, it adopts a provided interface that specifies the services that other components can utilize, and how they can do so. This interface can be seen as a signature of the component - the client does not need to know about the inner workings of the component (implementation) in order to make use of it. This principle results in components referred to as encapsulated.
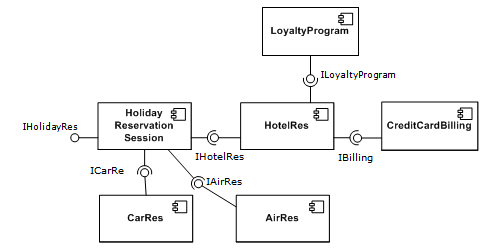
A simple example of several software components
pictured within a hypothetical holiday-reservation
system represented in UML 2.0.
Distributed and Paralel computing
A distributed system is a system whose components are located on different networked computers, which communicate and coordinate their actions by passing messages to one another. The components interact with one another in order to achieve a common goal. Three significant characteristics of distributed systems are: concurrency of components, lack of a global clock, and independent failure of components.
A computer program that runs within a distributed system is called a distributed program. There are many different types of implementations for the message passing mechanism, including pure HTTP, RPC-like connectors and message queues
Distributed systems are groups of networked computers, which have the same goal for their work. The terms concurrent computing, parallel computing, and distributed computing have a lot of overlap, and no clear distinction exists between them. The same system may be characterized both as parallel and distributed; the processors in a typical distributed system run concurrently in parallel. Parallel computing may be seen as a particular tightly coupled form of distributed computing, and distributed computing may be seen as a loosely coupled form of parallel computing
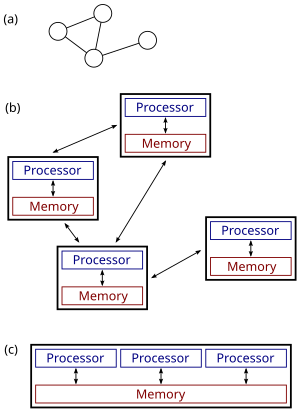
(a), (b): a distributed system.
(c): a parallel system.
Data Entities
A data entity is an abstraction from the physical implementation of database tables or collections.
A data entity is an object in a data model. Data is typically designed by breaking things down into their smallest parts that are useful for representing data relationships. For example, a customer may include a list of contacts. Each contact may contain an address. All three objects: customer, contact and address are considered data entities.
A data entity may also be a representation of a file from file system.
Service Layer pattern
Basically, Service layers are a bunch of actions/procedures that handles a specified Data Entity on server.
A “service layer” exists between the UI and the backend systems that store data, and is in charge of managing the business rules of transforming and translating data between those two layers.
JoborJob Resource Object
We call Job, any task that is going to be executed, on any time, inside a Distributed Computing environment.
In other words, It Is a data object that represents a end user request to perform an action against a Data Entity (aka server resource) through a specified Service layer.
The end user request is input into the pipe via HTTP messages (Rest APIs) or AMQP messages (Workers)
RPCorRemote Procedure Calls
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) is a protocol that one program can use to request a service from a program located in another computer on a network without having to understand the network’s details. A procedure call is also sometimes known as a function call or a subroutine call. RPC uses the client-server model.
In other words, RPC is the method where you access/consume/map remote server resources and it handlers.